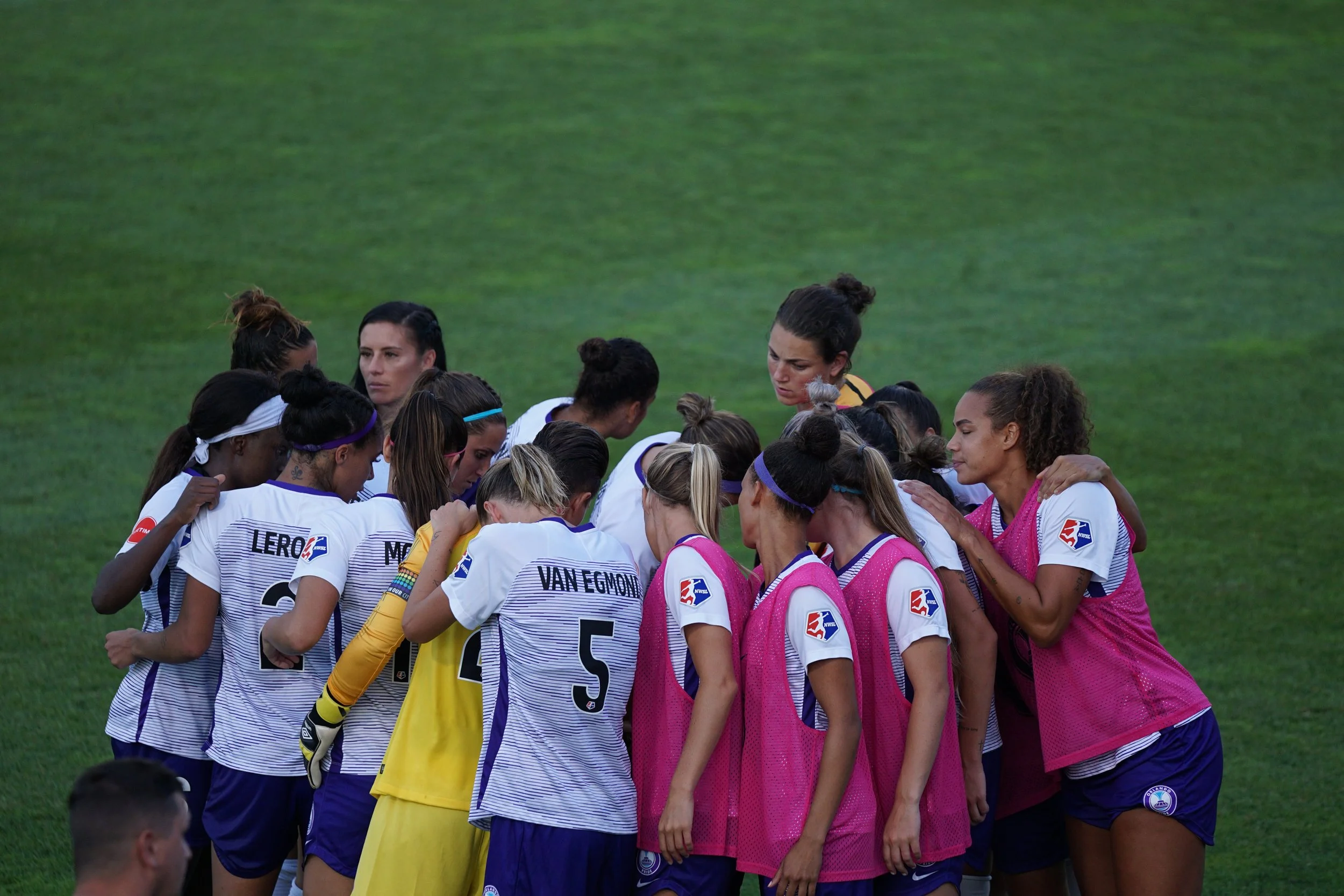
Elite sport is not immune to shifts in cultural norms and conventions in wider society. The number of diversity and inclusion roles have increased 60% in the UK over the past five years, and this has started to be mirrored in sporting organisations. The governance and national sport systems for Olympic sports are government funded, so it perhaps unsurprising that these organisations might be prompted to adopt policy that is becoming the norm in other sectors. That said, professional sports have also begun to follow this trend, notably in the US. In this post we consider what diversity and inclusion means in the context of sport at elite level.
Where Do We Draw the Line in Elite Sport?
Recent scandals, including multiple allegations and criminal cases of serious abuse, have rocked sport around the world. Arguably the most egregious example is the case of USA gymnastics, which should serve as a cautionary tale for everybody involved in sport at all levels. Against this backdrop, there has been something of an avalanche of allegations of bullying and improper conduct that are presently playing out in the public sphere. In turn, this has prompted calls for national sporting bodies to be less obsessively driven by winning medals. The perils of the ‘winning at all costs’ mentality have been cited as the reason behind the toxic environments and climate of fear that has been alleged in multiple sports, notably in the investigations that are presently ongoing within the UK. But of course winning on the world stage does come at a cost, both financial and personal. So where should we draw the line?
Rehabilitation and Return to Performance Following Injury
In elite and professional sports there is obvious incentive to ensure athletes make a prompt and successful return to action following injury. There is a clear impetus to push the envelope in an attempt to accelerate the recovery process and minimise the time spent on the sidelines. The impressive recovery times reported with common injuries in professional sports are testimony to the success of the progressive and innovative approaches presently employed. In a ‘high performance’ setting athletes benefit from having a staff of professionals at their disposal on a daily basis to support the endeavour. Given such dedicated support it is perhaps unsurprising that athletes at the top level also show a far higher likelihood of making a successful return to their preinjury level following severe injuries such as ACL rupture, compared to what is reported with performers at lower levels of competition. The stakes involved might differ below the elite level but there are nevertheless lessons to be learned from their approach to performance rehabilitation and return to competition. In this latest offering we explore the advances in how we deal with sports injuries and consider what lessons we might adopt to improve outcomes for performers at all levels.
First Do No Harm: Iatrogenics in Coaching and Practice
Iatrogenics is a term most commonly used in medicine. As attested by the Hippocratic oath (and the premise ‘First Do No Harm’), the medical profession is familiar with the concept that an intervention may pose potential risks and unforeseen consequences. In contrast, the idea that we may either not be helping or through our involvement inadvertently making the athlete worse off does not necessarily occur to coaches and practitioners. In this post we explore how iatrogenics applies in the context of coaching and practice, and make the case for considering potential risks as well as benefits before we intervene.
Marshalling the Mind Under Stress
High stakes and heightened emotions are characteristic of competitive sport, particularly at the highest level. For those who operate in elite and professional sport the presence of stress seems ubiquitous. Coaches and athletes alike regularly face high pressure scenarios where there is a great deal of expectation and much riding on the outcome. Anticipation of an important event, such as a big game, major competition, or selection trials naturally inspire a host of feelings, thoughts, and emotions, ranging from excitement to anxiety and even dread, sometimes simultaneously! In this post we explore how we can equip ourselves and help our athletes to meet the psychological and emotional challenges we will inevitably face on the journey.
Tempering Athletes: Future Proofing Versus Acquired Fragility
Tempering is a process used to impart strength and toughness, and essentially serves to bring out the intrinsic properties of the material under stress. Athletes forged in the crucible of severely testing conditions may be similarly rendered highly resilient to future challenges and stressors. Those who successfully come through such trial by fire paradoxically often prove stronger from the experience. The notion that stressors can not only make systems more resilient, but in fact stronger and better as a consequence, speaks to the concept of antifragility, a phenomenon observed in nature and highlighted by Nassim Taleb who famously coined the term. In this post, we will bring this antifragility lens, and a general reticence to accept that sports injuries ‘just happen’, to reframe how we think about preparing athletes to ‘future proof’ them to risks and scenarios that we cannot fully anticipate. In place of safeguarding measures and interventions that seek to protect, we will make the argument for tempering athletes to harness and develop their intrinsic reserves and coping abilities. Adopting this perspective and general strategy for managing injury risk, we will outline some tactics to help guide practitioners in their approach.