The initiative and intrinsic motivation to train solo successfully for extended periods are rare and vital qualities for any aspiring performer. Over recent months the lack of direct coaching supervision, restricted access to training facilities and absence of training partners posed huge challenges for athletes at all levels, testing not only their will but also their ability to find a way. Regular readers will recognise that these are not new themes - as noted before the biggest test of a coach is what happens when we’re not present. With the unprecedented events of 2020 all of this very much came to the fore. The critical role of agency and the need to ensure that athletes are capable of functioning independently are arguably among the biggest lessons that coaches, practitioners and indeed the athletes themselves can take from this tumultuous period.
What You See Is Not All There Is
To explain the title, one of the most common cognitive biases in how we see the world is encapsulated as ‘what you see is all there is’. In other words, we have a tendency to overlook what is not immediately visible or obvious. We tend to assume that what we see in full view constitutes the only aspects at play. We are slow to consider that there might be additional unseen factors at work that might lead us to an alternative explanation for what we are seeing. In most circumstances we are dealing with incomplete information and there is always some degree of uncertainty and ambiguity involved in human performance. These are not bugs in the system that must be fixed, but rather features that we need to learn to navigate.
Tackling Innovation in Elite Sport
An outsider’s view of elite and professional sport tends to assume that these environment are constantly engaged in ‘pushing the envelope’ in the relentless pursuit of better. The situation in reality tends to be quite different. Conventions and the pressure to conform to what others are doing have a powerful pull. Paradoxically the resistance to exploration and barriers to innovation are often more pronounced the highest level. Especially within professional sport those involved are acutely aware that their position is highly prized and job security at a premium. These conditions are naturally not conducive to taking risks or moving beyond the tried and tested. All of this helps to explain the abundant examples demonstrating that opportunities remain to gain significant competitive advantages and even some easy wins
Diversity and Inclusion in Elite Sport
Elite sport is not immune to shifts in cultural norms and conventions in wider society. The number of diversity and inclusion roles have increased 60% in the UK over the past five years, and this has started to be mirrored in sporting organisations. The governance and national sport systems for Olympic sports are government funded, so it perhaps unsurprising that these organisations might be prompted to adopt policy that is becoming the norm in other sectors. That said, professional sports have also begun to follow this trend, notably in the US. In this post we consider what diversity and inclusion means in the context of sport at elite level.
Beyond the Bubble: The Utility of a Neutral Third Party
One of the problems with our natural preference for those who think as we do is the tendency to find ourselves in an echo chamber. Leaders can of course combat this by recruiting for cognitive diversity, but even within a diverse group our thinking inevitably tends to become socialised as a natural consequence of spending time in the company of the same group of people. Our colleagues will also to some degree share the same biases and are subject to the conventions that are inherent to the sport. Professional sport in particular is a bubble - at present quite literally, but even under usual circumstances. It follows that it is important that we escape the bubble periodically. A related countermeasure is to strategically enlist a neutral third party to break up the usual routine and expose team members to perspectives from outside the bubble at regular intervals. Engaging with an outsider can serve a performance staff in a number of different ways as we will explore.
Where Do We Draw the Line in Elite Sport?
Recent scandals, including multiple allegations and criminal cases of serious abuse, have rocked sport around the world. Arguably the most egregious example is the case of USA gymnastics, which should serve as a cautionary tale for everybody involved in sport at all levels. Against this backdrop, there has been something of an avalanche of allegations of bullying and improper conduct that are presently playing out in the public sphere. In turn, this has prompted calls for national sporting bodies to be less obsessively driven by winning medals. The perils of the ‘winning at all costs’ mentality have been cited as the reason behind the toxic environments and climate of fear that has been alleged in multiple sports, notably in the investigations that are presently ongoing within the UK. But of course winning on the world stage does come at a cost, both financial and personal. So where should we draw the line?
Realities of 'Performance Consulting'
It is increasingly prevalent for forward-thinking individuals within various organisations to seek insights from other domains and explore novel practices that have been applied with success elsewhere. Coming in as an outsider also allows the separation and distance that is necessary to offer an objective assessment of where things currently stand. In either scenario it is becoming more widely recognised that there is merit in seeking out different perspectives. A different way of considering the problem naturally opens up new possibilities for solutions. One route to achieving this cognitive diversity is via recruitment and employing individuals different backgrounds importing expertise from overseas bring experiences from other sports. An alternative strategy as we will explore is to engage individuals in a consulting capacity.
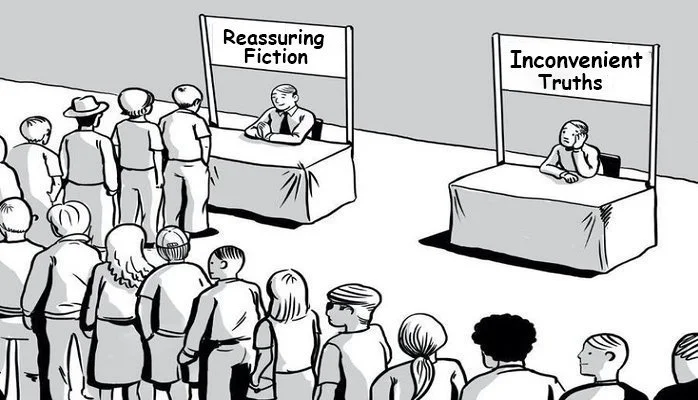
Triangulating a Position
As the value of cognitive diversity becomes more recognised, what is striking is how slow we have been to realise the need to revise our habitual ways of consuming information and interacting with those who hold contrary views. Whilst pioneers who think different are celebrated in modern western culture, in reality we are far less amenable to entertaining disagreement and diverging ideas. In the professional and academic realm we are quick to follow an authority and align with a school of thought. The hordes are likewise quick to leap into the breach to defend the doctrine against perceived challenge or dissenting views. If anything debates in all circles are increasingly polarised, as the assembled masses flock to either one side or the other. We might appreciate cognitive diversity on a conceptual level, but on a practical level we are clearly not there yet. So what steps can we take to enjoy the benefits of cognitive diversity and open our minds to the possibilities as we form our opinions?
First Do No Harm: Iatrogenics in Coaching and Practice
Iatrogenics is a term most commonly used in medicine. As attested by the Hippocratic oath (and the premise ‘First Do No Harm’), the medical profession is familiar with the concept that an intervention may pose potential risks and unforeseen consequences. In contrast, the idea that we may either not be helping or through our involvement inadvertently making the athlete worse off does not necessarily occur to coaches and practitioners. In this post we explore how iatrogenics applies in the context of coaching and practice, and make the case for considering potential risks as well as benefits before we intervene.