Coaching is characterised as a judgement and decision making process. Practitioners and indeed most professionals who work in human performance are de facto coaches of humans. As such, the quest that unites coaches in different sports and practitioners across disciplines is to develop our professional judgement and our ability to make better choices and decisions over time. There is no endpoint to this journey and so the need to continually hone our judgement and decision making applies irrespective of what stage we are might be at in our career. That said, the question of how we best develop these skills for practitioners at the start of their career versus catering for these aspects in continuing professional development thereafter will likely require different solutions.
Continuing Our Education
As many practitioners will testify, it is after we have completed our formal education, professional training and certification that the real learning begins. The day to day experience of solving problems with live humans is when we discover the limits of our knowledge. It is also here that we find out that the reality is quite different to what is taught in class and the version that appears in (most) textbooks. Individuals, organisations and certifying bodies alike recognise this need to continue our learning once we are working in our respective field. The terms continuing education, continuing professional development and variations thereof will be familiar to most practitioners across disciplines (sadly it is not so well established in the coaching profession). What is less clear is how we might best tackle this ongoing quest and make good choices from the growing array of options with regards to content and the modes of delivery that are available to us.
Rejecting the Industry
Practitioners across different domains will be familiar with their field of practice being referred to as an 'industry'. We frequently hear mention of the strength and conditioning industry, the sports physiotherapy industry, even the sports coaching industry. In this post we consider these trends for terming our professions in this way, and explore why an 'industry approach' might be problematic. From these discussions we can attempt to plot a path back to cultivating our craft, and restoring pride in our chosen profession by rejecting this ‘industry’ mindset.
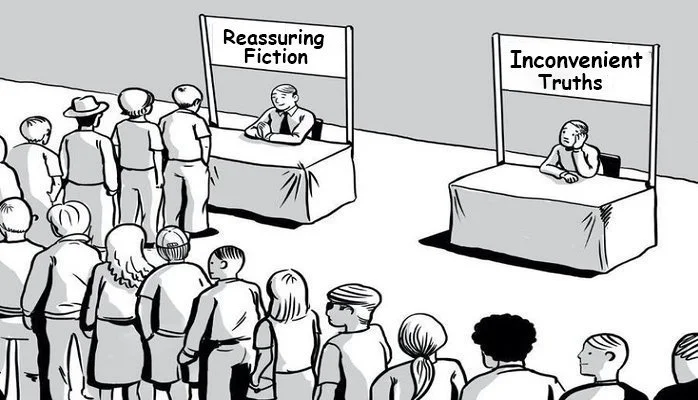
Resurrecting Critical Thinking
In the Information Age the propensity for critical thinking has become arguably the most critical skill for practitioners in all fields. In the present era, with unprecedented access to a vast sea of information at the touch of a key stroke, the ability to filter and to critically evaluate are paramount. This is the great irony of the Information Age; at a time when the need has never been greater, critical thinking is seemingly a dying art. Increasingly we are plagued with superficial knowledge and incomplete understanding. We are beset on all sides by spurious reasoning and a preponderance of facile solutions. In this post we argue there is a need to resurrect critical thinking; we must understand the true meaning of skepticism and embrace it. Here we present the case that rediscovering these faculties will allow us to negotiate our way to free thought and provide the tools for independent learning to attain deeper understanding.
The Puzzle of Programming Training for Humans
I regularly engage in mentoring coaches and practitioners, and the universal starting point in this process is a 'SWOT analysis', allowing the individual to identify areas where they require development. A frequent response and common theme relates to the process of planning or programming training. Before we get into the puzzles to solve when programming physical preparation, let us begin with a revelation: athletes are humans not machines. Input does not necessarily equal output. When working with athletes we must understand that we are dealing with inherently complex and highly dynamic biological systems. Designing a training plan for an athlete or a group of athletes is therefore far from straightforward.
In this post we will unmask the flaws in the conventional wisdom that relates to planning and programming, including periodisation models. We will uncover the realities we face when programming training, explore the puzzles involved, and define the challenges we must resolve. Finally, we will outline a road map approach to guide planning physical preparation in a way that acknowledges the uncertainty, along with some strategies to help navigate the unknown and shifting terrain, to allow us to steer and adapt our course as we go.
Mobilising Athletes' Mental Resources During Training
Ask any athlete or coach and they will readily acknowledge the mental side of training. The mind is an integral part of training the body. How an athlete perceives the training prescribed can be hugely influential in determining how they experience it. In turn this perception can affect how the athlete responds to the training performed. Despite their apparent importance, mental aspects of the training process are typically not accounted for in any structured or meaningful way. In this post we will elucidate what these critical elements or 'mental resources' are in relation to the training process. We will then explore how each of these aspects can be accounted for and harnessed to best effect in the way athletes' training plans are presented and delivered.
What do we mean by 'Athletic'? The 10 Pillars of Athleticism
Practitioners working in the realms of physical preparation, 'strength and conditioning', athletic development, sports coaching and sports medicine all share the desire that their athletes become more 'athletic'. Feats of athleticism can be readily recognised and appreciated. Yet observers and practitioners alike would struggle to describe with any clarity or detail what exactly constitutes 'athleticism'. Clearly we must first define qualities such as athleticism in order to understand how we might go about developing them. From a talent identification and talent development viewpoint, what do we need to identify and develop in a young athlete? In this post we aim to elucidate what athleticism is, and explore the constituent parts that underpin athleticism.
The Olympic Pursuit of Inspiration
For the most part, when those in the media talk of 'inspiration' or 'being inspired' they are referring to those watching sport being inspired to strive to achieve the feats that they have seen or attempt to emulate sporting heroes. In this way, great athletes are often described as 'an inspiration to others'. Essentially, this is inspiration borne of admiration - essentially the 'I want to be like them when I grow up' scenario.
The alternative meaning of inspiration - and the definition that this post will mostly focus on - is inspiration in the sense of stimulating thought or inspiring new ideas.
Specificity and the Simulation Trap
This week I was asked about sport-specific programming by a young coach. Specificity is much misunderstood or at best incompletely understood in relation to training prescription and programming. Our task is to prepare the athlete for the rigours of training and competing. Nonetheless, rather than training the sport into the individual, we train the individual in the sport. In this sense the sport (or sports) provides the context, but the focus remains tailoring physical preparation and athletic development to the individual. This is a subtle but important distinction as we will explore in this post.
The Simplicity and Complexity Paradox in Training and Coaching
In a presentation last year I used the concept of yin and yang to describe the inter-relationship between physical and technical in track and field athletics. In essence, yin and yang describes how opposing elements (light and dark, fire and water) paradoxically serve to complement and ultimately define each other. Much the same applies when considering simplicity versus complexity. There are many instances where each of these elements apply in the realms of coaching and various facets of practice in elite sport. In this post we will explore the paradoxical - or yin and yang - relationship between simplicity versus complexity in the fields of coaching, physical preparation and sports injury.